Introduction
POWERSYS performed for a utility located in North America a voltage transient analysis. The scope of work concerned a medium voltage substation where frequent voltage dips (10/20%) have been reported. This substation is located at the end of a radial transmission line and near two other substations equipped with capacitor banks and powering large industries.
The goals of the study included:
- To investigate the origin of the voltage dips,
- To review the capacitor bank coordination settings to validate them or suggest new operational solutions to limit the voltage dips.
The industries in the vicinity are composed of static and dynamic loads such as large induction machine.

Figure 1: Electrical substation

Figure 2: Several water pumps with large electric motors
Challenge and Methodology
The first task was to model the upstream networks and the loads to understand the origins of the voltage dips.
It was proposed to use EMTP® to model the entire system. Therefore, a dynamic model is constructed in EMTP® . The model contains all the in-scope equipment including an upstream network Thevenin equivalent, the capacitor banks, the substations and the loads. Steady-state and dynamic load data (low, medium and peek) are estimated from the data measured by the power quality and revenue meters. Characteristics of the large induction machine in the industries were provided.
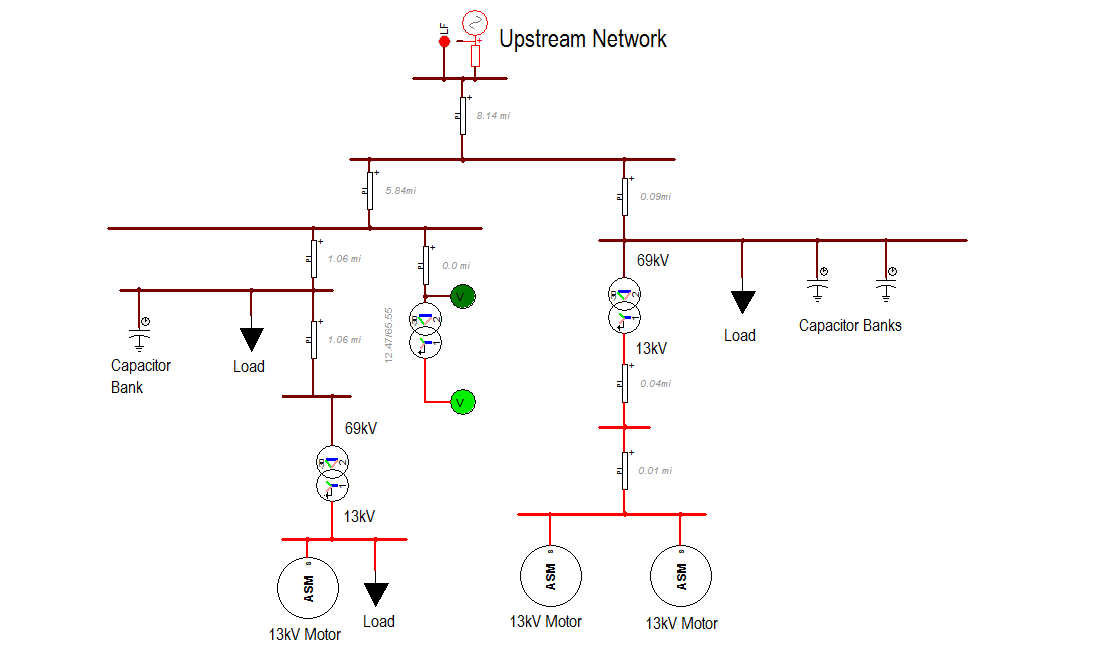
Figure 3: Simplified one-line diagram
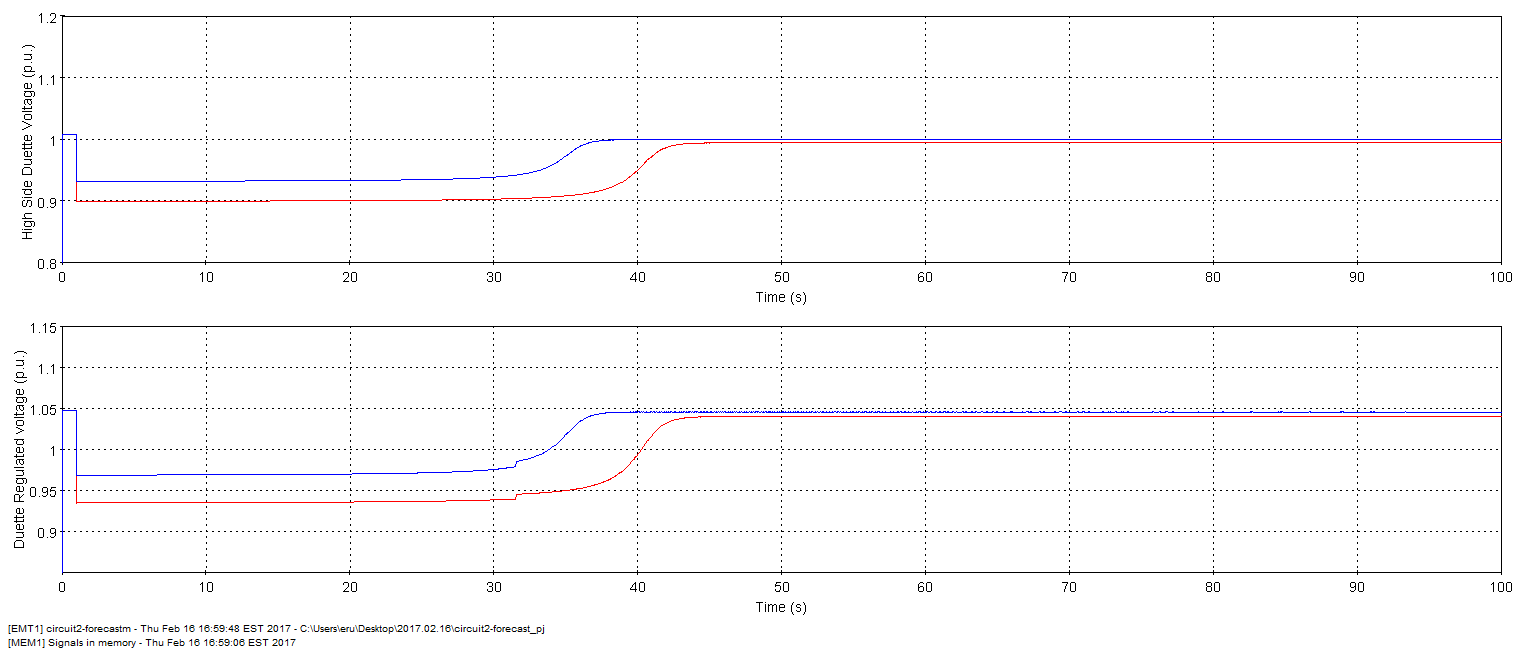
A parametric study is performed using the JavaScript scripting capabilities of EMTP® . It consists in analysing the voltage dip caused by the starting of large induction machines. Steady-state loads are varied and different type of induction machines are started.
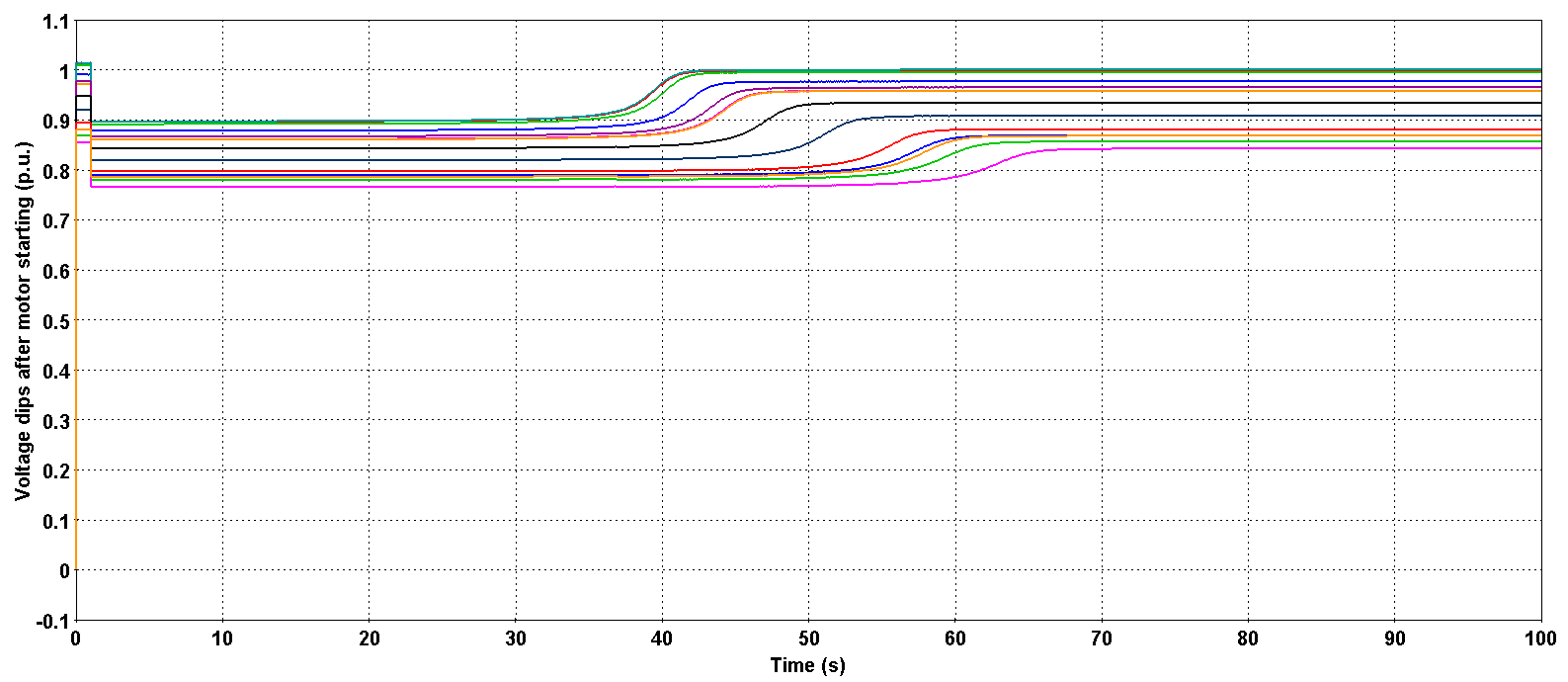
Figure 4: Example of voltage dips due to motor starting
Various mitigation techniques are investigated and proposed to limit the voltage sags:
- Adding a Static Var Compensator (SVC) is an effective technical solution to boost the voltage and reduce voltage dips.
- Another solution, more economically viable, would be to reduce the operation time of capacitor banks. A controlled-switching device can achieve a better level of performance. This technology consists in reducing inrush current when closing the circuit breakers by considering the residual voltage and by optimizing the switching times. Therefore, a capacitor bank can be operated several times per seconds. Controlled-switching can be added to existing capacitor banks or included in a new system.
Conclusion and Perspective
Thanks to EMTP®, the origin of the voltage dips is identified. Various mitigation measures are proposed and validated through simulation.
We stay at your disposal if you have any questions about transient studies or how we can assist your company. Our high-skilled team will work closely with you from the definition of the project to the delivery of the engineering study to achieve its successful completion. Our experience in the power systems industry combined with the quality of EMTP® contributes to our worldwide reputation.
At Powersys we offer through our associated staff a wide range of consulting and power systems engineering services using state of the art technologies to help you address new and emerging problems related to power system engineering.