Access to EMTP user presentations, webinars, and slide deck presentations.
page 2 of 2
9 presentations for inverter-based resources:

Author(s): Husam Samkari & Rafael Castillo Sierra
Type:On-demand webinars
Date: 2022-02-17
Slideshow of the projects from our grand prize winners857
Abstract
During this webinar, our two winners of the EMTP® Research Contribution Prize Program 2021 will present their work. The aim of the award is to recognize student contributions to the technology associ... see moreated with power system transients. The two competition categories are:
- Best accepted IEEE, IET, PSCC, EPSR or IPST journal or conference paper on EMT simulations;
- Best EMTP® model developed.
Discover our winner and the topics of their presentation:
o Husam Samkari, Ph.D. and P.E. in Electrical Engineering
Impact of Distributed Inverter-Based Resources on Incremental Quantities-Based Protection
Abstract:
This paper studies the impact of distributed inverter-based resources (IBR) on time-domain incremental quantities-based relays. One implementation of the incremental quantities for protection is a high-speed sub-cycle directional element. The incremental, also known as superimposed, quantities are fault-generated instantaneous components of voltages and currents. The directional element indicates fault direction based on the transient voltages and currents’ relative polarities. It is essential to ensure that the element does not fail to indicate the correct direction if IBRs fault current responses impact the quantities. IBRs’ fast control response impacts the current quantities by changing both magnitude and angle.
This paper characterizes the incremental quantities-based relay response to IBRs’ nonlinear fault currents. A modified IEEE 34-bus distribution with an IBR system is modeled and simulated using the electromagnetic transients program (EMTP) for demonstration.
o Rafael Castillo Sierra, Electrical Engineer, Ph.D. Student
Model category for his model on Power System with a Transmission Line operating at low frequency
Abstract:
The transmission of electric power with alternating current (AC) faces constraints that are inherent both to the stable operation of the power system and to the physical properties of the transmission lines or cables. Many factors stand to motivate the alleviation of these constraints without a need to construct new transmission lines or cables. One demonstrated method to accomplish this is to lower the electrical frequency of a transmission branch or section of the network, an approach known as low frequency AC (LFAC) transmission. The resulting lower reactance of the lines improves the transmission under the stability concerns which arise with long, inductive overhead lines, as well as under thermal concerns that can be substantial due to charging currents in underground cables. In this order of ideas, the Modular Multilevel Matrix Converter (MMMC) offers the necessary frequency conversion for low-frequency transmission, while allowing controllability of power through the transmission line.
For this reason, this presentation focuses on the EMTP modeling and simulation of this converter starting from a design that meets the typical voltage and power requirements for a transmission line. The averaged model of the converter has been implemented to evaluate its performance as a frequency converter and how it interacts with the power system. Simulations have been carried out under nominal operating conditions in a study case power system.
Tag(s): EMTP, Prize winners, IBR, Protection, Power system, Transmission Line, Low frequency,

Author(s): Karine Gauthier, Pascal Prud’homme, Saad Omar and Henry Gras
Type:On-demand Webinars
Date: 2021-05-06
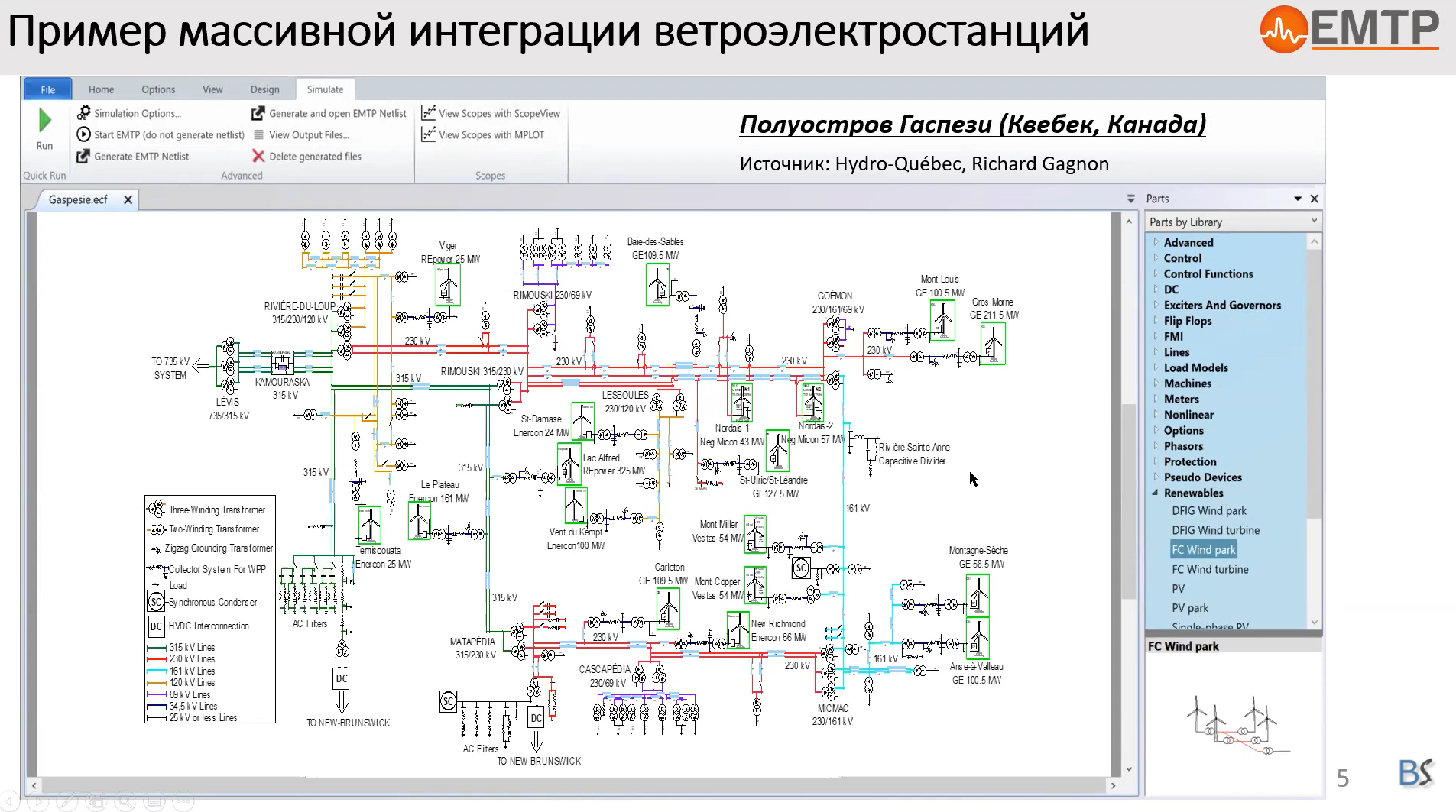
EMTP® studies for IBR integration at Hydro-Quebec777
Abstract
Abstract:
Hydro-Quebec has been involved in EMTP® development since the 80s and has collaborated with several organizations worldwide through the Development Coordination Group of EMTP (DC... see moreG-EMTP). Hydro-Quebec was the key player in the EMTP recoding project that allowed the delivery of the latest generation of the software in 2003. The new EMTP was developed at IREQ (Hydro-Quebec’s research center) from 1998 to 2003.
Hydro-Quebec was the first organization to simulate its complete transmission grid in EMTP. Hydro-Quebec was also the first system operator to require that manufacturers of wind turbines provide detailed EMT-type (EMTP®) models for wind park integration studies. This webinar will present:
• How EMTP simulations are integrated into Hydro-Quebec’s work process?
• How EMTP simulations can complete RMS simulations?
• Future simulation challenges
Speakers:
• Karine Gauthier, ing.
• Pascal Prud’homme, ing.
• Saad Omar, ing.
Tag(s): inverter-based resources, IBR, model validation, large scale

Author(s): Evangelos Farantatos, Electric Power Research Institute (EPRI)
Type:Technical Presentation
Date: 2020-11-20
Impact of Wind & Solar Generation on Negative Sequence and Power Swing Protection741
Abstract
<h6 class="text-black" style="padding-bottom: 30px; padding-top: 30px; text-align: justify;">Speaker: <strong>Evangelos Farantatos&l... see moret;/strong>, <em>Electric Power Research Institute (EPRI)</em></h6> <p class="text-black">Inverter-based resources have much more complex fault current characteristics compared to conventional synchronous generators. Hence, legacy protective relays set under the assumption of a conventional power system with predominantly synchronous generation, may misoperate under high level of renewables.<br><br> This presentation first investigates the impact of wind generation on the performance of negative-sequence-based protection. In many applications, wind generators are designed to suppress negative sequence current partially or entirely. Negative sequence current suppression control may result in the misoperation of protection schemes whose operation relies on the assumption of negative sequence quantities being present in substantial levels during unbalanced faulted conditions. The impact of wind generation on negative-sequence overcurrent and negative-sequence-based directional elements is investigated in this work.<br> In addition, the impact of renewable resources on the performance of power swing protection is investigated. Case studies with examples of Power Swing Blocking (PSB) and Out-of-Step Tripping (OST) elements misoperation under wind generation will be presented.</p>

Author(s): Aboutaleb Haddadi, Polytechnique Montréal & Afshin Rezaei-Zarei, York University
Type:Technical Presentation
Date: 2020-11-20
Geomagnetic disturbance simulation studies: recent developments and challenges738
Abstract
<h6 class="text-black" style="padding-bottom: 30px; padding-top: 30px; text-align: justify;">Speaker: <strong>Aboutaleb Haddadi</... see morestrong>, <em>Polytechnique Montréal</em></h6> <p class="text-black">Inverter-based resources have much more complex fault current characteristics compared to conventional synchronous generators. Hence, legacy protective relays set under the assumption of a conventional power system with predominantly synchronous generation, may misoperate under high level of renewables.<br><br> This presentation first investigates the impact of wind generation on the performance of negative-sequence-based protection. In many applications, wind generators are designed to suppress negative sequence current partially or entirely. Negative sequence current suppression control may result in the misoperation of protection schemes whose operation relies on the assumption of negative sequence quantities being present in substantial levels during unbalanced faulted conditions. The impact of wind generation on negative-sequence overcurrent and negative-sequence-based directional elements is investigated in this work.<br> In addition, the impact of renewable resources on the performance of power swing protection is investigated. Case studies with examples of Power Swing Blocking (PSB) and Out-of-Step Tripping (OST) elements misoperation under wind generation will be presented.</p>






![[R&D]_EMTP : Recherche et développement [R&D]_EMTP : Recherche et développement](https://www.emtp.com/system/files/imagecache/presentation/slide1_1.jpg)




![[Protection_Devices]_Étude des courants coupés par les sectionneurs de changemen [Protection_Devices]_Étude des courants coupés par les sectionneurs de changemen](https://www.emtp.com/system/files/imagecache/presentation/TechnicalPresentation1.jpg)
