Access to EMTP user presentations, webinars, and slide deck presentations.
150 presentations for EMTP:
Author(s): Moez Belhaouane, L2EP-Ecole Centrale de Lille
Type:Technical Presentation
Date: 2020-11-20
Abstract
<h2 class="title">EMTP Europe User Conference 2019 </h2> <p class="tagline"><b>The EMTP User Conference pres... see moreentations are now available online!</b></p> <p id="text-intro"><b>Electromagnetic Transients (EMT) Model Design Based on Modular Multilevel Converter Mockup</b><br> A detailed EMT model for MMC (Modular Multilevel Converter) has been realized using EMTP software. The aim is to present the modelling process, from the identification of the MMC element parameters, to the conception of the measurement process. The last part of the presentation will compare the EMTP model to the experimental behavior for different operating points.
Author(s): Evangelos Farantatos, Electric Power Research Institute (EPRI)
Type:Technical Presentation
Date: 2020-11-20
Abstract
<h6 class="text-black" style="padding-bottom: 30px; padding-top: 30px; text-align: justify;">Speaker: <strong>Evangelos Farantatos&l... see moret;/strong>, <em>Electric Power Research Institute (EPRI)</em></h6> <p class="text-black">Inverter-based resources have much more complex fault current characteristics compared to conventional synchronous generators. Hence, legacy protective relays set under the assumption of a conventional power system with predominantly synchronous generation, may misoperate under high level of renewables.<br><br> This presentation first investigates the impact of wind generation on the performance of negative-sequence-based protection. In many applications, wind generators are designed to suppress negative sequence current partially or entirely. Negative sequence current suppression control may result in the misoperation of protection schemes whose operation relies on the assumption of negative sequence quantities being present in substantial levels during unbalanced faulted conditions. The impact of wind generation on negative-sequence overcurrent and negative-sequence-based directional elements is investigated in this work.<br> In addition, the impact of renewable resources on the performance of power swing protection is investigated. Case studies with examples of Power Swing Blocking (PSB) and Out-of-Step Tripping (OST) elements misoperation under wind generation will be presented.</p>
Author(s): Manuel Martinez & Paul Poujade, EDF
Type:Technical Presentation
Date: 2020-11-20
Abstract
<h2 class="title">EMTP Europe User Conference 2019 </h2> <p class="tagline"><b>The EMTP User Conference pres... see moreentations are now available online!</b></p> <p id="text-intro"><b>Transformer Energization Study Case with PAMSUITE</b><br> A number of EMTP studies require parametric simulations. It is namely the case for transformer energization where many uncertain parameters can greatly influence the simulation results. This presentation will show how these kinds of studies can be quickly and easily carry out with PAMSUITE, the EMTP toolbox for parametric studies.
Author(s): Ulas Karaagac, Hong Kong Polytechnic University
Type:Technical Presentation
Date: 2020-11-20
Abstract
<h6 class="text-black" style="padding-bottom: 30px; padding-top: 30px; text-align: justify;">Speaker: <strong>Ulas Karaagac</stro... see moreng>, <em>Hong Kong Polytechnic University</em></h6> <p class="text-black">Subsynchronous control interaction (SSCI) is the interaction between the power electronics control and the series compensated transmission system that occurs at frequencies below the system nominal frequency. SSCI may occur between the doubly-fed induction generator (DFIG) control system and the series compensated transmission line, to which the wind park (WP) is connected. Not only the DFIG control system parameters, but also the WP operating conditions have significant impact on SSCI.<br><br>This presentation will demonstrate the impact of WP operating conditions and DFIG control system parameters on SSCI. Guidelines will be also presented for modifying the DFIG control system parameters to ensure safe operation and acceptable transient responses due to faults. In addition, the accuracies of various analytical tools used for SSCI problem identification will be discussed.</p>
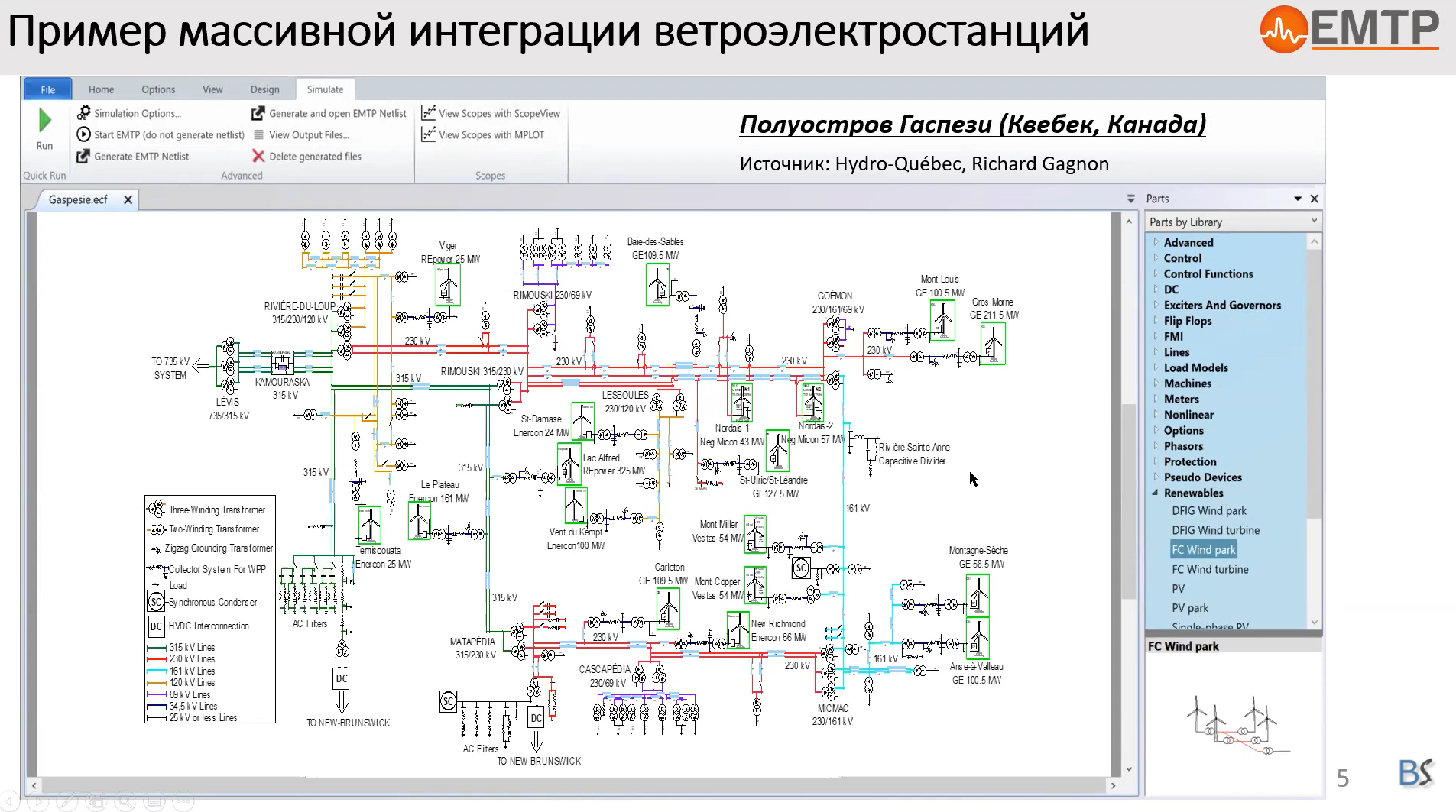
Author(s): Ilhan Kocar, Polytechnique Montréal
Type:Technical Presentation
Date: 2020-11-20
Abstract
<h6 class="text-black" style="padding-bottom: 30px; padding-top: 30px; text-align: justify;">Speaker: <strong>Ilhan Kocar</strong... see more>, <em>Polytechnique Montréal</em></h6> <p class="text-black">The new WB model encapsulates many improvements including state-of-the-art research results. It eliminates the modeling problems encountered with the existing universal line model (ULM) approach.<br> In the new model, there is no limitation on the number of conductors. For symmetric coaxial cable systems with several cables, numerical problems are avoided by using the new cable correction function. The newly added DC correction scheme together with frequency band partitioning ensures high precision both at low frequencies and high frequencies. Frequency partitioning also improves the numerical conditioning of the system of equations. Unrealistic delays are avoided thanks to the new routines for the identification and adjustment of time delays. The delay adjustment is a search routine with boundaries for optimized fitting.<br><br> The state space formulation in time domain is reformulated using a precise discrete integration method. It minimizes the numerical integration and interpolation errors. This allows achieving stable simulations with larger time steps. The object oriented programming approach with vectorized variables and new memory allocation routines significantly improves the simulation speed and use of memory. The new initialization routines allow seamless transition from steady state solution into time domain simulations.</p></div>












![[R&D]_EMTP : Recherche et développement [R&D]_EMTP : Recherche et développement](https://www.emtp.com/system/files/imagecache/presentation/slide1_1.jpg)




![[Protection_Devices]_Étude des courants coupés par les sectionneurs de changemen [Protection_Devices]_Étude des courants coupés par les sectionneurs de changemen](https://www.emtp.com/system/files/imagecache/presentation/TechnicalPresentation1.jpg)
